How to configure unattended upgrades on Debian. How to Configure Automated Security Updates on Debian.
As part of the security it is important to keep your system up to date. With the unattended-upgrades utility you can automatically update and upgrade the system on a daily basis.
Update and upgrade first
Before we start we will update and upgrade the system
Log in via SSH
SSH root@x.x.x.xReplace x.x.x.x for the ip address of your server.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall Unattended Upgrades
- Install unattended-upgrades
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades- 2. Start the
unattended-upgradesservice by running the following commands:
sudo systemctl enable unattended-upgrades
sudo systemctl start unattended-upgradesYou can now check the status:
systemctl status unattended-upgrades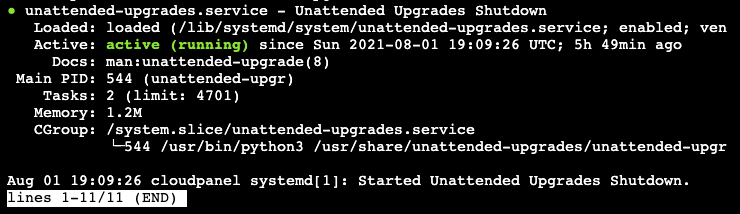
Use ctrl+z to stop the status display.
Configure Unattended Upgrades
To configure the kind of (security) updates we need to edit the following file:
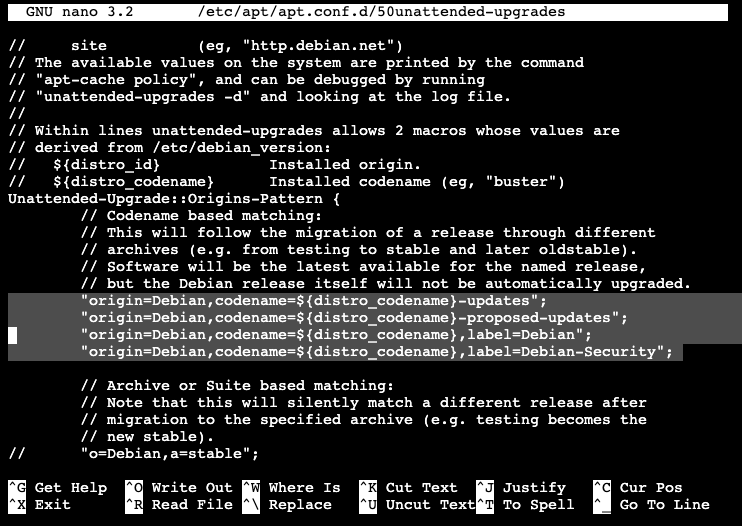
/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgradesBe sure that the following lines are uncommented in order to get all updates:
"origin=Debian,codename=${distro_codename}-updates";
"origin=Debian,codename=${distro_codename}-proposed-updates";
"origin=Debian,codename=${distro_codename},label=Debian";
"origin=Debian,codename=${distro_codename},label=Debian-Security";
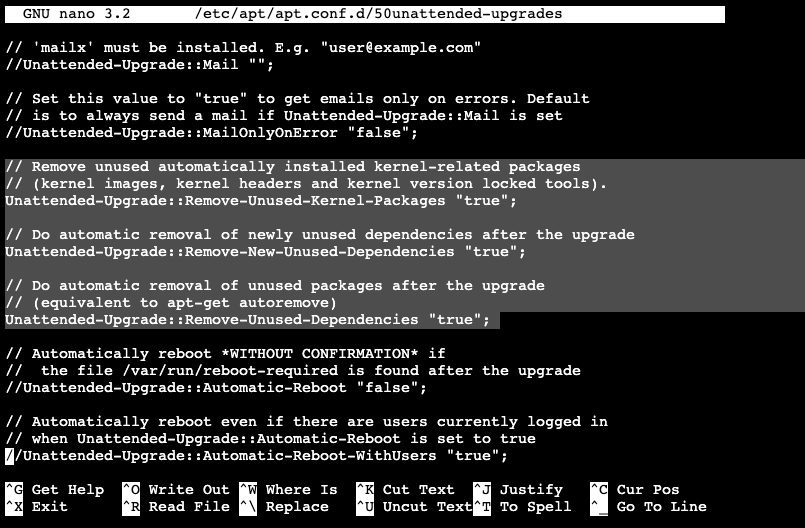
Set Remove-Unused-Kernel-Packages, Remove-New-Unused-Dependencies, and Remove-Unused-Dependencies options to true.
Enabling Automatic Upgrades
To enable automatic updates create a new auto-upgrades file: /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
Paste the following lines in the file:
APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "1"; APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "1"; APT::Periodic::AutocleanInterval "7";

Testing The Configuration
You can run the dry run test by using the command:
sudo unattended-upgrades --dry-run --debugLogfiles
The log files are located at:
/var/log/unattended-upgrades
